economy
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Provided by
Years
Formats
Scale
Resolution
-
The technical harvesting potential of logging residues and stumps from final fellings can be defined as the maximum potential procurement volume of these available from the Finnish forests based on the prevailing guidelines for harvesting of energy wood. The potentials of logging residues and stumps have been calculated for fifteen NUTS3-based Finnish regions covering the whole country (Koljonen et al. 2017). The technical harvesting potentials were estimated using the sample plots of the eleventh national forest inventory (NFI11) measured in the years 2009–2013. First, a large number of sound and sustainable management schedules for five consecutive ten-year periods were simulated for each sample plot using a large-scale Finnish forest planning system known as MELA (Siitonen et al. 1996; Redsven et al. 2013). MELA simulations consisted of natural processes and human actions. The ingrowth, growth, and mortality of trees were predicted based on a set of distance-independent tree-level statistical models (e.g. Hynynen et al. 2002) included in MELA and the simulation of the stand (sample plot)-level management actions was based on the current Finnish silvicultural guidelines (Äijälä et al. 2014) and the guidelines for harvesting of energy wood (Koistinen et al. 2016). Final fellings consisted of clear cutting, seed tree cutting, and shelter-wood cutting, but only the clear-cutting areas were utilized for energy wood harvesting. As both logging residues and stumps are byproducts of roundwood removals, the technical potentials of chips have to be linked with removals of industrial roundwood. Future potentials were assumed to materialize when the industrial roundwood fellings followed the level of maximum sustainable removals. The maximum sustainable removals were defined such that the net present value calculated with a 4% discount rate was maximized subject to non-declining periodic industrial roundwood and energy wood removals and net incomes, and subject to the saw log removal remaining at least at the level of the first period. There were no constraints concerning tree species selection, cutting methods, age classes, or the growth/drain ratio in order to efficiently utilize the dynamics of forest structure. The felling behaviour of the forest owners was not taken into account either. For the present situation in 2015, the removal of industrial roundwood was assumed to be the same as the average level in 2008–2012. Fourth, the technical harvesting potentials were derived by retention of 30% of the logging residues onsite (Koistinen et al. 2016) and respectively by retention of 16–18% of stump biomass (Muinonen et al. 2013). Next, the regional potentials were allocated to municipalities proportionally to their share of mature forests (MetINFO 2014). Subsequently, the municipality-level potentials were spread evenly on a raster grid at 1 km × 1 km resolution. Only grid cells on Forests Available for Wood Supply (FAWS) were considered in this operation. Here, FAWS was defined as follows: First, forest land was extracted from the Finnish Multi-Source National Forest Inventory (MS-NFI) 2013 data (Mäkisara et al. 2016). Second, restricted areas were excluded from forest land. The restricted areas consisted of nationally protected areas (e.g. nature parks, national parks, protection programme areas). References Äijälä O, Koistinen A, Sved J, Vanhatalo K, Väisänen P (2014) Metsänhoidon suositukset [Guidelines for sustainable forest management]. Metsätalouden kehittämiskeskus Tapion julkaisuja. Hynynen J, Ojansuu R, Hökkä H, Salminen H, Siipilehto J, Haapala P (2002) Models for predicting the stand development – description of biological processes in MELA system. The Finnish Forest Research Institute Research Papers 835. Koistinen A, Luiro J, Vanhatalo K (2016) Metsänhoidon suositukset energiapuun korjuuseen, työopas [Guidelines for sustainable harvesting of energy wood]. Metsäkustannus Oy, Helsinki. Koljonen T, Soimakallio S, Asikainen A, Lanki T, Anttila P, Hildén M, Honkatukia J, Karvosenoja N, Lehtilä A, Lehtonen H, Lindroos TJ, Regina K, Salminen O, Savolahti M, Siljander R (2017) Energia ja ilmastostrategian vaikutusarviot: Yhteenvetoraportti. [Impact assessments of the Energy and Climate strategy: The summary report.] Publications of the Government´s analysis, assessment and research activities 21/2017. Mäkisara K, Katila M, Peräsaari J, Tomppo E (2016) The Multi-Source National Forest Inventory of Finland – methods and results 2013. Natural resources and bioeconomy studies 10/2016. Muinonen E, Anttila P, Heinonen J, Mustonen J (2013) Estimating the bioenergy potential of forest chips from final fellings in Central Finland based on biomass maps and spatially explicit constraints. Silva Fenn 47. Redsven V, Hirvelä H, Härkönen K, Salminen O, Siitonen M (2013) MELA2012 Reference Manual. Finnish Forest Research Institute. Siitonen M, Härkönen K, Hirvelä H, Jämsä J, Kilpeläinen H, Salminen O, Teuri M (1996) MELA Handbook. Metsäntutkimuslaitoksen tiedonantoja 622. ISBN 951-40-1543-6.
-
The raw materials of forest chips in Biomass Atlas are small-diameter trees from first thinning fellings and logging residues and stumps from final fellings. The harvesting potential consists of biomass that would be available after technical and economic constraints. Such constraints include, e.g., minimum removal of energywood per hectare, site fertility and recovery rate. Note that the techno-economic potential is usually higher than the actual availability, which depends on forest owners’ willingness to sell and competitive situation. The harvesting potentials were estimated using the sample plots of the 11th and 12th national forest inventory (NFI11 and NFI12) measured in the years 2013–2017. First, a large number of sound and sustainable management schedules for five consecutive ten-year periods were simulated for each sample plot using a large-scale Finnish forest planning system known as MELA (Siitonen et al. 1996; Hirvelä et al. 2017). MELA simulations consisted of natural processes and human actions. The ingrowth, growth, and mortality of trees were predicted based on a set of distance-independent tree-level statistical models (e.g. Hynynen et al. 2002) included in MELA and the simulation of the stand (sample plot)-level management actions was based on the current Finnish silvicultural guidelines (Äijälä et al. 2014) and the guidelines for harvesting of energy wood (Koistinen et al. 2016). Future potentials were assumed to materialize when the industrial roundwood fellings followed the level of maximum sustainable removals (80.7 mill. m3 in this calculation). The maximum sustainable removals were defined such that the net present value calculated with a 4% discount rate was maximized subject to non-declining periodic industrial roundwood and energy wood removals and net incomes, and subject to the saw log removal remaining at least at the level of the first period. There were no constraints concerning tree species selection, cutting methods, age classes, or the growth/drain ratio in order to efficiently utilize the dynamics of forest structure. The potential for energywood from first thinnings was calculated separately for all the wood from first thinnings (Small-diameter trees from first thinnings) and for material that does not fulfill the size-requirements for pulpwood (Small-diameter trees from first thinnings, smaller than pulpwood). The minimum top diameter of pulpwood in the calculation was 6.3 cm for pine (Pinus sylvestris) and 6.5 cm for spruce (Picea abies) and broadleaved species (mainly Betula pendula, B. pubescens, Populus tremula, Alnus incana, A. glutinosa and Salix spp.). The minimum length of a pulpwood log was assumed at 2.0 m. The potentials do not include branches. The potentials for logging residues and stumps were calculated as follows: The biomass removals of clear fellings were obtained from MELA. According to harvesting guidelines for energywood (Koistinen et al. 2016) mineral soils classified as sub-xeric (or weaker) and peatlands with corresponding low nutrient levels were left out from the potentials. Finally, technical recovery rates were applied (70% for logging residues and 82-84% for stumps) (Koistinen et al. 2016; Muinonen et al. 2013) The techno-economical harvesting potentials were first calculated for nineteen Finnish regions and then distributed on a raster grid at 1 km × 1 km resolution by weighting with Multi-Source NFI biomasses as described by Anttila et al. (2018). The potentials represent time period 2025-2034 and are presented as average annual potentials in solid cubic metres over bark. References Äijälä O, Koistinen A, Sved J, Vanhatalo K, Väisänen P. 2014. Metsänhoidon suositukset. [Guidelines for sustainable forest management]. Metsätalouden kehittämiskeskus Tapion julkaisuja. Anttila P., Nivala V., Salminen O., Hurskainen M., Kärki J., Lindroos T.J. & Asikainen A. 2018. Regional balance of forest chip supply and demand in Finland in 2030. Silva Fennica vol. 52 no. 2 article id 9902. 20 s. https://doi.org/10.14214/sf.9902 Hirvelä, H., Härkönen, K., Lempinen, R., Salminen, O. 2017. MELA2016 Reference Manual. Natural Resources Institute Finland (Luke). 547 p. Hynynen J, Ojansuu R, Hökkä H, Salminen H, Siipilehto J, Haapala P. 2002. Models for predicting the stand development – description of biological processes in MELA system. The Finnish Forest Research Institute Research Papers. 835. Koistinen A, Luiro J, Vanhatalo K. 2016. Metsänhoidon suositukset energiapuun korjuuseen, työopas. [Guidelines for sustainable harvesting of energy wood]. Tapion julkaisuja. Muinonen E., Anttila P., Heinonen J., Mustonen J. 2013. Estimating the bioenergy potential of forest chips from final fellings in Central Finland based on biomass maps and spatially explicit constraints. Silva Fennica 47(4) article 1022. https://doi.org/10.14214/sf.1022. Siitonen M, Härkönen K, Hirvelä H, Jämsä J, Kilpeläinen H, Salminen O et al. 1996. MELA Handbook. 622. 951-40-1543-6.
-
The technical harvesting potential of small-diameter trees can be defined as the maximum potential procurement volume of small-diameter trees available from the Finnish forests based on the prevailing guidelines for harvesting of energy wood. The potentials of small-diameter trees from early thinnings have been calculated for fifteen NUTS3-based Finnish regions covering the whole country (Koljonen et al. 2017). To begin with the estimation of the region-level potentials, technical harvesting potentials were estimated using the sample plots of the eleventh national forest inventory (NFI11) measured in the years 2009–2013. First, a large number of sound and sustainable management schedules for five consecutive ten-year periods were simulated for each sample plot using a large-scale Finnish forest planning system known as MELA (Siitonen et al. 1996; Redsven et al. 2013). MELA simulations consisted of natural processes and human actions. The ingrowth, growth, and mortality of trees were predicted based on a set of distance-independent tree-level statistical models (e.g. Hynynen et al. 2002) included in MELA and the simulation of the stand (sample plot)-level management actions was based on the current Finnish silvicultural guidelines (Äijälä et al. 2014) and the guidelines for harvesting of energy wood (Koistinen et al. 2016). Simulated management actions for the small-tree fraction consisted of thinnings that fulfilled the following stand criteria: • mean diameter at breast height ≥ 8 cm • number of stems ≥ 1500 ha-1 • mean height < 10.5 m (in Lapland) or mean height < 12.5 m (elsewhere). Energy wood was harvested as delimbed (i.e. including the stem only) in spruce-dominated stands and peatlands and as whole trees (i.e. including stem and branches) elsewhere. When harvested as whole trees, a total of 30% of the original crown biomass was left onsite (Koistinen et al. 2016). Energy wood thinnings could be integrated with roundwood logging or carried out independently. Second, the technical energy wood potential of small trees was operationalized in MELA by maximizing the removal of thinnings in the first period. In this way, it was possible to pick out all small tree fellings simulated in the first period despite, for example, the profitability of the operation. However, a single logging event was rejected if the energy wood removal was lower than 25 m³ha-1 or the industrial roundwood removal of pine, spruce, or birch exceeded 45 m³ha-1. The potential calculated in this way contained also timber suitable for industrial roundwood. Therefore, two estimates are given: • potential of trees below 10.5 cm in breast-height diameter • potential of trees below 14.5 cm in breast-height diameter. Subsequently, the region-level potentials were spread on a raster grid at 1 km × 1 km resolution. Only grid cells on Forests Available for Wood Supply (FAWS) were considered in this operation. In this study, FAWS was defined as follows: First, forest land was extracted from the Finnish Multi-Source National Forest Inventory (MS-NFI) 2013 data (Mäkisara et al. 2016). Second, restricted areas were excluded from forest land. The restricted areas consisted of nationally protected areas (e.g. nature parks, national parks, protection programme areas) and areas protected by the State Forest Enterprise. In addition, some areas in northernmost Lapland restricted by separate agreements between the State Forest Enterprise and stakeholders were left out from the final data. Furthermore, for small trees, FAWS was further constrained by the stand criteria presented above to represent similar stand conditions for small-tree harvesting as in MELA. Finally, the region-level potentials were distributed to the grid cells by weighting with MS-NFI stem wood biomasses. References Äijälä O, Koistinen A, Sved J, Vanhatalo K, Väisänen P (2014) Metsänhoidon suositukset [Guidelines for sustainable forest management]. Metsätalouden kehittämiskeskus Tapion julkaisuja. Hynynen J, Ojansuu R, Hökkä H, Salminen H, Siipilehto J, Haapala P (2002) Models for predicting the stand development – description of biological processes in MELA system. The Finnish Forest Research Institute Research Papers 835. Koistinen A, Luiro J, Vanhatalo K (2016) Metsänhoidon suositukset energiapuun korjuuseen, työopas [Guidelines for sustainable harvesting of energy wood]. Metsäkustannus Oy, Helsinki. Koljonen T, Soimakallio S, Asikainen A, Lanki T, Anttila P, Hildén M, Honkatukia J, Karvosenoja N, Lehtilä A, Lehtonen H, Lindroos TJ, Regina K, Salminen O, Savolahti M, Siljander R (2017) Energia ja ilmastostrategian vaikutusarviot: Yhteenvetoraportti. [Impact assessments of the Energy and Climate strategy: The summary report.] Publications of the Government´s analysis, assessment and research activities 21/2017. Mäkisara K, Katila M, Peräsaari J, Tomppo E (2016) The Multi-Source National Forest Inventory of Finland – methods and results 2013. Natural resources and bioeconomy studies 10/2016. Redsven V, Hirvelä H, Härkönen K, Salminen O, Siitonen M (2013) MELA2012 Reference Manual. Finnish Forest Research Institute. Siitonen M, Härkönen K, Hirvelä H, Jämsä J, Kilpeläinen H, Salminen O, Teuri M (1996) MELA Handbook. Metsäntutkimuslaitoksen tiedonantoja 622. ISBN 951-40-1543-6.
-
Metsähakkeen korjuupotentiaali kuvaa metsähakkeen raaka-aineiden teknistä hankintamahdollisuutta. Raaka-aineina tässä aineistossa on huomioitu 1) uudistushakkuilta korjattavat hakkuutähteet eli latvusmassa ja kannot sekä 2) nuorten metsien pienpuu. Tekninen potentiaali tarkoittaa sitä osaa latvusmassasta, kannoista ja pienpuusta, joka on erilaisten rajoitteiden aiheuttamien vähennysten jälkeen korjattavissa. Tällaisia rajoitteita ovat mm. korjuukohteen hehtaarikohtainen energiapuun vähimmäiskertymä, poistettavan rungon keskimääräinen vähimmäiskoko, kasvupaikka ja talteensaantoaste. Tekninen potentiaali ei kuvaa metsähakkeen saatavuutta, joka riippuu mm. metsänomistajan myyntihalukkuudesta ja kilpailutilanteesta. Aineistot on kuvattu suppeasti alla ja tarkemmin Anttilan ym. (2013, 2014) raporteissa. Pienpuupotentiaalit perustuvat valtakunnan metsien 10. inventoinnin (VMI10) koealatietoihin (Korhonen ym. 2013). Koealat on mitattu vuosina 2004-2008, ja kattavat koko maan poislukien Ylä-Lapin. Pienpuuta korjataan energiaksi lähinnä varttuneista taimikoista sekä nuorten kasvatusmetsien ensiharvennuksilta, joten tarkastelu rajoitettiin näiden kehitysluokkien koealoihin. Koealoista valittiin ne, joille oli maastoinventoinnissa ehdotettu taimikonhoitoa tai ensiharvennusta seuraavan viiden vuoden kuluessa. Koealoille simuloitiin alaharvennus Tapion metsänhoitosuositusten (Hyvän metsähoidon suositukset 2006) mukaisesti. Joka koealalle laskettiin runkopuun poistuma ja ainespuun kertymä puulajeittain (mänty, kuusi ja koivu) rinnankorkeusläpimitaltaan yli neljä senttimetriä paksuista puista. Kuitupuupölkyn lyhin sallittu pituus oli kaksi metriä ja minimilatvaläpimitta 6 cm. Rinnankorkeusläpimitaltaan 4-9,5 cm:n puut laskettiin puulajista riippumatta kokonaan energiapuuksi. Pienpuulle laskettiin potentiaalit kuntakohtaisesti olettaen kolme eri korjuumenetelmää. Kaikissa menetelmissä energiapuun minimikertymän koealalla tuli olla vähintään 25 m3/ha. Puhtaissa energiapuuvaihtoehdoissa (menetelmät Ranka ja Kokopuu) ainespuun kertymälle asetettiin enimmäisrajaksi 45 m3/ha, jonka ylittävät koealat katsottiin ainespuukohteiksi. Nimensä mukaisesti vaihtoehdossa Ranka laskettiin pelkän rangan potentiaali ja vaihtoehdossa Kokopuu mukaan laskettiin myös elävät oksat. Aines- ja energiapuun integroituun korjuuseen (menetelmä Integroitu) soveltuviksi taas katsottiin puhtaat havupuu- ja koivukoealat, joilla pääpuulajin ainespuun kertymä oli suurempi kuin 20 m3/ha, kertymän keskirunkokoko suurempi kuin 30 dm3 ja energiajakeen kertymä suurempi kuin 25 m3/ha. Energiajae oletettiin korjattavaksi rankana, koska ainespuu korjataan karsittuna ja energiapuu korjataan samalla kalustolla. Tavaralajipuhtaaksi koeala luettiin, mikäli havupuiden tai koivun ainespuukertymä oli yli 80 % koealan ainespuukertymästä. Jos ainespuun kertymä oli pienempi tai yhtä suuri kuin 20 m3/ha, kohde oletettiin korjattavaksi energiakäyttöön kokopuuna. Kaikissa vaihtoehdoissa runkopuun ja elävän latvuksen tekniseksi talteensaannoksi olettiin 100 %. Kokopuukorjuussa kuolleiden oksien sen sijaan oletettiin varisevan korjuun ja kuljetuksen aikana. Uudistushakkuilta kertyvän latvus- ja kantobiomassan potentiaalit riippuvat uudistushakkuiden määrästä, joka puolestaan riippuu puunjalostusteollisuuden kotimaisen puun tarpeesta. Uudistushakkuille syntyvän latvus- ja kantobiomassan määrän arviot perustuvat kahteen eri ainespuun hakkuumahdollisuusarvioon: Suurin kestävä aines- ja energiapuun hakkuukertymä (SK) ja Toteutunut hakkuukertymä (TH). Arviot tuotettiin MELA-mallilla (Redsven ym. 2013). Hakkuumahdollisuusarviot perustuivat vuosien 2008–2012 aikana mitattuihin valtakunnan metsien inventoinnin maastokoealoihin (http://www.metla.fi/metinfo/vmi/). Kunkin metsäkeskuksen alueelle suurin puuntuotannollisesti ja taloudellisesti jatkuvasti hakattavissa oleva puumäärä on laskettu maksimoimalla nettotulojen nykyarvoa neljän prosentin laskentakorolla siten, että kausittaiset nettotulot ja aines- ja energiapuun hakkuukertymät pysyvät vähintään edellisen kymmenvuotiskauden tasolla, tukkipuukertymä säilyy koko laskelma-ajan vähintään ensimmäisen kauden tasolla, ja puuston tuottoarvo neljän prosentin korkokannalla laskettuna on laskelma-ajan lopussa vähintään alkuhetken tasolla (laskelma SK). Laskelmassa ei rajoitettu kasvun ja poistuman suhdetta, metsien ikäluokkarakennetta tai uudistushakkuiden määrää eikä kestävyyttä edellytetty puulajeittain. Toteutuneet hakkuut (TH) -laskelmassa ainespuun kertymä puulajeittain ja uudistushakkuupinta-ala säilyivät vuoteen 2050 asti vuosien 2008–2012 keskimääräisellä tasolla. Laskelmista TH ja SK poimittiin hakkuupoistuman biomassat avohakkuilta runkopuulle, oksille ja kannoille. Mukaan luettiin korjuuohjeiden mukaisesti vain kuivahkot kankaat ja niitä viljavammat kivennäismaat sekä vastaavat turvemaat (Äijälä ym. 2010). Latvusmassan poistuma arvioitiin lisäämällä oksabiomassaan runkopuun hukkaosuus. Latvus- ja kantobiomassa muunnettiin kiintotilavuudeksi jakamalla kunkin jakeen biomassa vastaavalla kuivatuoretiheydellä. Lopulta tekninen korjuupotentiaali saatiin vähentämällä edellisestä palstalle suositusten mukaan jätettävä osuus (latvusmassalla 30 % ja kannoilla 16-18 %). Metsäkeskustason potentiaalit jaettiin edelleen kunnille niiden uudistuskypsien metsien pinta-alaosuuden mukaan (MetINFO 2014). Kuntatason potentiaalit levitettiin tasan vuoden 2013 maaluokkatulkinnan mukaiselle metsämaalle (Avoimien aineistojen tiedostopalvelu 2015), josta oli poistettu luonnonsuojelualueet (Avoin tieto 2016). Viitteet Anttila, P., Nivala, M., Laitila, J. & Korhonen, K.T. 2013. Metsähakkeen alueellinen korjuupotentiaali ja käyttö. Metlan työraportteja / Working Papers of the Finnish Forest Research Institute 267. 24 s. Saatavissa: http://www.metla.fi/julkaisut/workingpapers/2013/mwp267.htm. Anttila, P., Nivala, M., Laitila, J., Flyktman, M., Salminen, O. & Nivala, J. 2014. Metsähakkeen alueellinen korjuupotentiaali ja käyttö vuonna 2020. Metlan työraportteja / Working Papers of the Finnish Forest Research Institute 313. 55 s. Saatavissa: http://www.metla.fi/julkaisut/workingpapers/2014/mwp313.htm. Avoin tieto. 2016. Internet-portaali. Suomen ympäristökeskus. Saatavissa: http://www.syke.fi/avointieto. Avoimien aineistojen tiedostopalvelu. 2015. Internet-portaali. Luonnonvarakeskus. Saatavissa: http://kartta.metla.fi/. Hyvän metsänhoidon suositukset. 2006. Metsätalouden kehittämiskeskus Tapio. ISBN 13-978-952-5118-84-1. Korhonen, K.T., Ihalainen, A., Viiri, H., Heikkinen, J., Henttonen, H.M., Hotanen, J.-P., Mäkelä, H., Nevalainen, S. & Pitkänen, J. 2013. Suomen metsät 2004–2008 ja niiden kehitys 1921–2008. Metsätieteen aikakauskirja 3/2013: 269–608. MetINFO. 2014. MetINFO – Metsätietopalvelut. Saatavissa: http://www.metla.fi/metinfo. Redsven, V., Hirvelä, H., Härkönen, K., Salminen, O., Siitonen, M. 2013. MELA2012 Reference Manual (2nd edition). Finnish Forest Research Institute. 666 p. (Saatavilla: http://mela2.metla.fi/mela/julkaisut/oppaat/mela2012_2nd_ed.pdf). Äijälä, O., Kuusinen, M. & Koistinen, A. 2010. Hyvän metsänhoidon suositukset energiapuun korjuuseen ja kasvatukseen. Metsätalouden kehittämiskeskus Tapio. 31 s. Saatavissa: http://www.tapio.fi/files/tapio/Aineistopankki/Energiapuusuositukset_verkkoon.pdf.
-
Metsähallituksen ennallistamat ojitusalueet Pohjois-Satakunnan osalta.
-
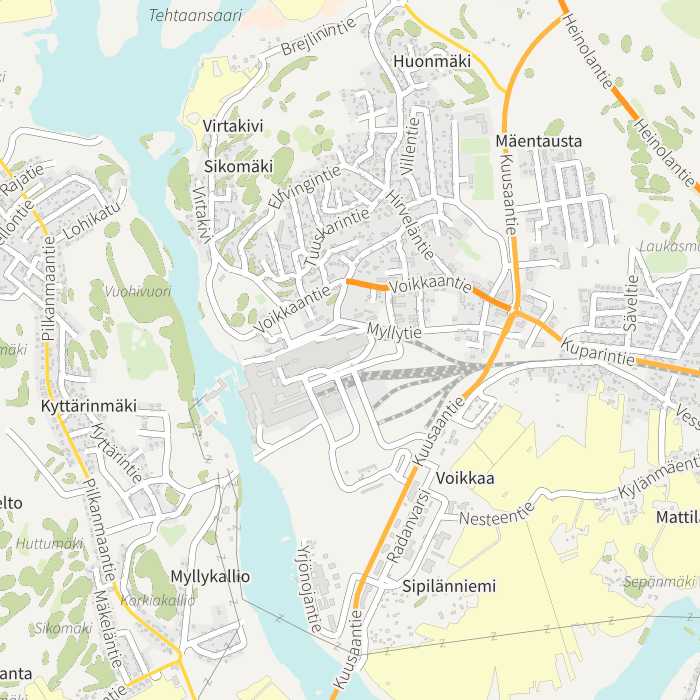
CGI:n NS-taustasarja on selkeä ja hillityn pelkistetty. Se soveltuu varsinkin tilastolliseen tarkasteluun ja temaattisten esitysten tueksi. Asutusalueet korostuvat rakennusten korkeuden mallintamisella. Kartta-aineisto jatkuu Suomen ulkopuolelle globaalina aineistona, jossa paikannimistönä on hyödynnetty OpenStreetMap, Geonames -nimiaineistoa ja ESA Landcover -maankäyttöaineistoa. Taustakarttasarjan päälle voi rakentaa erilaisia web-palveluja. Aineiston tarkkuus ja tyylikäs visualisointi tuovat lisäarvoa verrattaessa ilmaisiin webissä saatavilla oleviin karttasarjoihin. CGI:n taustakartta on myös käyttöehdoiltaan selkeä vaihtoehto verrattaessa esimerkiksi Googlen aineistoon. Taustakartta-aineistot ovat saatavilla kuvaruutu -mittakaavoilla (1:5300 – 1:12M) sekä painokartta -mittakaavoilla (1:20k – 1:5M). Aineisto on julkinen, mutta käyttöoikeuslupa tarvitaan. Aineiston käyttö ja julkaiseminen on maksullista. Aineiston käyttöluvan voi tilata CGI:lta (support.lbs.fi@cgi.com)
 DEMO Paikkatietohakemisto
DEMO Paikkatietohakemisto